I like to keep running child packages inside sequence container even if one of them fails. Currently they are failing;
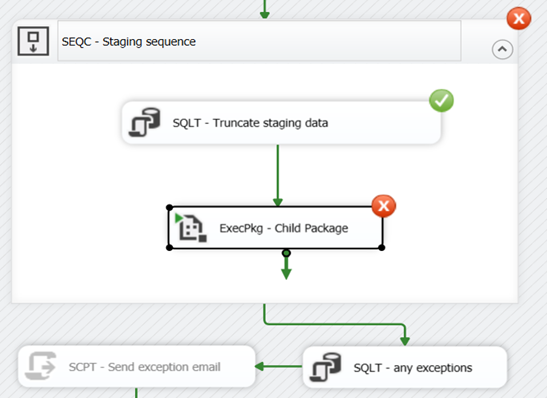
The work around is to set Sequence container “MaximumErrorCount” property to 2 from 1. After doing that, I am still getting failure error.
What we need to do is to fake the result assuming master and child packages have proper logging in place if they fail. Go to the Properties of “ExecPkg – Child Package” and set “ForceExecutionResult” to Success.
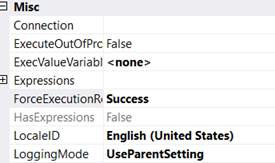
Do the same for master package. Run the package;
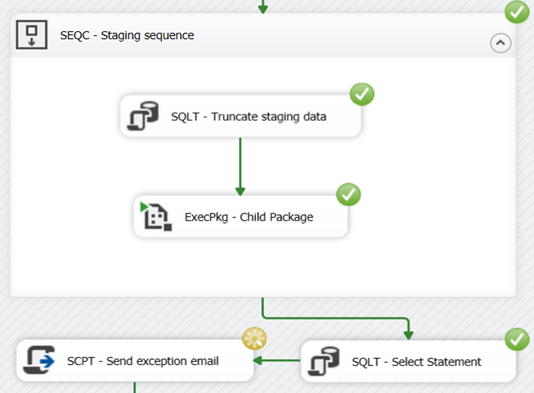
You can see that child package has no issues despite the fact that this has been failed. We can confirm that from log table if it’s enabled on package level.
These are the default values for a new container.
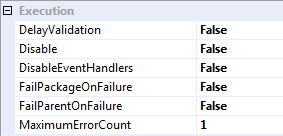
Now lets stop and study. If we compare the package behavior against the property settings, this looks wrong. Here we have set FailPackageOnFailure=False, yet a Sequence Container failure is causing a Package failure. Why is this? Unintuitive attribute names. See this Microsoft Connect issue. You are not alone in your confusion. The official explanation from Microsoft is this.
Despite some pretty circular previous messages, we believe that the feature is behaving as designed. When you set FailParentOnFailure to false, the parent will not fail until the number of failures in the child exceeds the MaximumAllowedErrors threshold. When you set FailparentOnFailure to true, the parent will fail on the first occurence of an error regardless of the MaximiumAllowedErrors threshold.