A practical guide for enforcing secure, identity-driven access to sensitive files
Organizations handling legal, regulatory, or citizen data often face a common challenge:
How do you ensure that only authorized roles can open sensitive documents—regardless of where the file travels?
The answer lies in document-level protection, not folder permissions.
With Microsoft Purview Sensitivity Labels, you can encrypt files and enforce role-based access using identity, ensuring protection stays with the document everywhere it goes.
Why Document-Level Protection Matters
Traditional access control depends on storage location:
- SharePoint permissions
- Folder restrictions
- Network access rules
But once a file is downloaded or shared, control weakens.
Sensitivity Labels solve this by:
- Encrypting documents
- Binding access to user identity
- Defining explicit roles (Viewer, Editor, Co-Owner)
- Enforcing protection across devices and locations
This model is especially valuable for:
- Legal and court records
- Government documentation
- HR and personnel files
- Financial reports
- Investigation materials
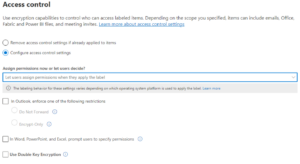
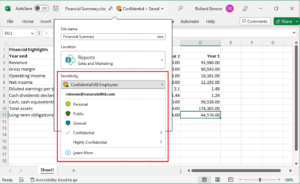
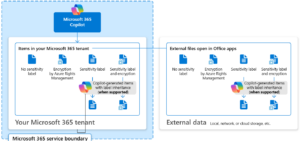
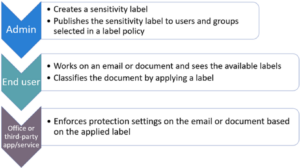
Sensitivity Labels apply encryption and define who can access a document and what actions they can perform.
Key characteristics:
✔ Protection travels with the file
✔ Access is identity-based
✔ Unauthorized users cannot bypass encryption
✔ Enforcement works across email, downloads, and cloud sharing
Step-by-Step: Configuring Role-Based Document Access
1️⃣ Create a Security Group
Start by defining authorized users in Microsoft Entra ID.
Example:
Security Group: District_Attorney_Authorized_Users
Members: District Attorney user accounts
This group becomes the foundation for permission enforcement.
2️⃣ Create a Sensitivity Label
In Microsoft Purview:
Label Name: Sealed – Court Record
Protection Setting: Enable encryption
Define explicit permissions:
| Role | Access Level |
|---|---|
| Judge (Owner) | Co-Owner |
| District Attorney Group | Viewer or Editor |
| Others | No Access |
3️⃣ Apply the Label
When the document owner classifies the file:
- The document becomes encrypted
- Only authorized roles can decrypt
- Unauthorized users are blocked automatically
Even if uploaded to Microsoft SharePoint or shared externally, protection remains intact.
What Unauthorized Users Experience
If someone outside the allowed roles attempts to open the file:
- They see an access denied message
- They cannot override encryption
- Admin roles do not bypass document-level protection
This ensures compliance and confidentiality.
Real-World Use Cases
✔ Sealed court records
✔ Law enforcement documentation
✔ Public sector investigations
✔ Contract negotiations
✔ Executive communications
This model supports compliance frameworks requiring strict confidentiality controls.
Key Takeaway
Sensitivity Labels provide identity-driven document protection, ensuring that:
🔐 Access is role-based
📁 Protection travels with the file
🌐 Storage location becomes irrelevant
🛡 Compliance and confidentiality remain intact
For public-sector and regulated environments, this is one of the most reliable ways to protect sensitive information at scale.
