After the data refresh (database restore), run this, otherwise the job would be failing;
USE MyDatabase;
GO
EXEC sp_change_users_login 'Update_One', 'MySchma', 'MyUser';
GO
EXEC sp_change_users_login 'Update_One', 'MySchema', 'MyUser';
GO
All about Azure Databases, Azure single database, Azure managed instance, Azure Cosmos database, Azure VM based databases
After the data refresh (database restore), run this, otherwise the job would be failing;
USE MyDatabase;
GO
EXEC sp_change_users_login 'Update_One', 'MySchma', 'MyUser';
GO
EXEC sp_change_users_login 'Update_One', 'MySchema', 'MyUser';
GO
We can use Regular Expression to find and replace, valid with all versions of SSMS
That regular expression indicates find everything and remember what we found Replace everything we found \1 by wrapping it with tic marks and a comma.
If you have more complex requirements, the right chevron next to the drop down arrow on Find what lists the regular expression dialect SSMS/Visual Studio understands
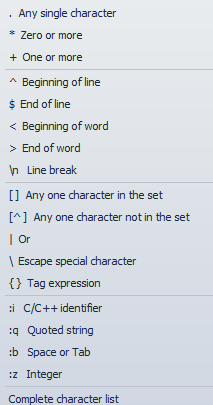
References
https://dba.stackexchange.com/questions/96371/applying-quotes-across-multiple-lines
Updating SSIS packages for a specific SQL server target version (valid only for SQL Server 2012 and above)
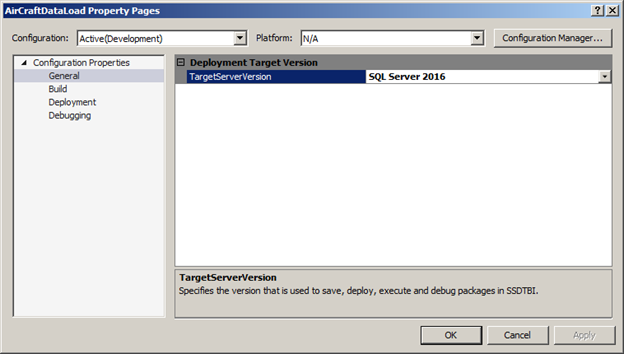
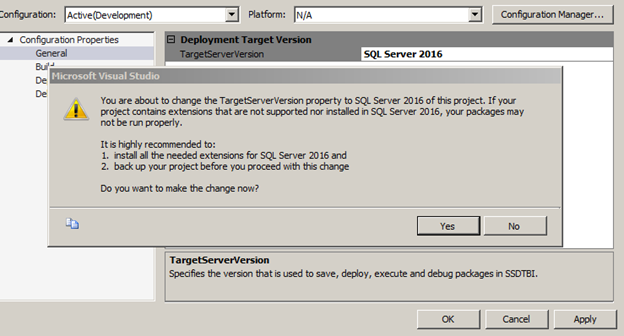
Click Apply, read the warning then click Yes as shown below, and finally click Ok
Re-open the packages and notice how the development platform (control flow and data flow tabs) changes
Before
After
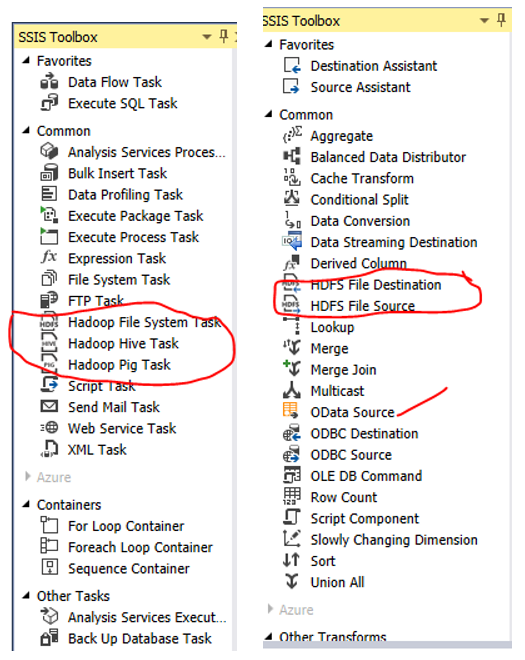
Check for any odd behavior (discontinued/deprecated tasks), build/rebuild your packages, test your packages, and deploy/redeploy them.
SQL Server 2012 has two new analytical functions, LEAD() AND LAG(). These functions return data from Next row (LEAD) and Previous row (LAG) of the same dataset without using self-join.
Let’s go with an example;
This is my initial dataset;
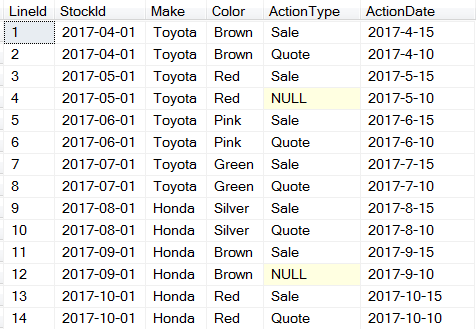
Here is the query to create this dataset;
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb..#SampleDataSet') is not null drop table #SampleDataSet
SELECT *
INTO #SampleDataSet
FROM
(
SELECT 1 LineId, '2017-04-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Brown' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-4-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 2 LineId, '2017-04-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Brown' AS Color, 'Quote' AS ActionType, '2017-4-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 3 LineId, '2017-05-01' StockId,'Toyota' AS Make, 'Red' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-5-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 4 LineId, '2017-05-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Red' AS Color, NULL AS ActionType, '2017-5-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 5 LineId, '2017-06-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Pink' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-6-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 6 LineId, '2017-06-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Pink' AS Color, 'Quote' AS ActionType, '2017-6-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 7 LineId, '2017-07-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Green' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-7-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 8 LineId, '2017-07-01' StockId, 'Toyota' AS Make, 'Green' AS Color, 'Quote' AS ActionType, '2017-7-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 9 LineId, '2017-08-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Silver' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-8-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 10 LineId, '2017-08-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Silver' AS Color, 'Quote' AS ActionType, '2017-8-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 11 LineId, '2017-09-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Brown' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-9-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 12 LineId, '2017-09-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Brown' AS Color, NULL AS ActionType, '2017-9-10' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 13 LineId, '2017-10-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Red' AS Color, 'Sale' AS ActionType, '2017-10-15' ActionDate UNION
SELECT 14 LineId, '2017-10-01' StockId, 'Honda' AS Make, 'Red' AS Color, 'Quote' AS ActionType, '2017-10-10' ActionDate
) src
WHERE 1=1
/*
This is my initial dataset
*/
SELECT * FROM #SampleDataSet src
I am adding SeqCount and Seq column to identify each group of car (make and color) and each action in the group. LAG and Lead values of LineId column are used to demonstrate function output.
SELECT
src.LineId, src.StockId,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY StockId ORDER BY ActionDate DESC) Seq,
COUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY StockId) SeqCount,
src.Make, src.Color, src.ActionType, src.ActionDate,
LEAD(src.LineId) OVER (ORDER BY src.LineId) LeadValue,
LAG(src.LineId) OVER (ORDER BY src.LineId) LagValue
FROM #SampleDataSet src
This is the output of above query;
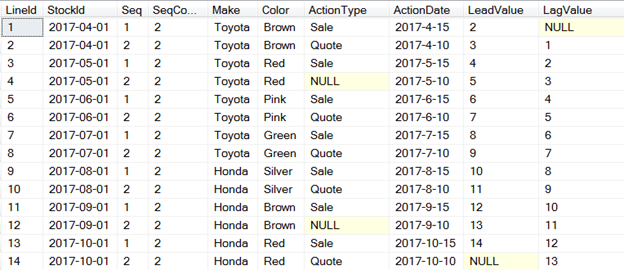
You can see the application of LEAD() and LAG() function in last two columns on the right side of above dataset.
One of the possible application of this function. As a business rule every quote action must be preceded by sale action in a car dealer dataset. If quote action is null in a group, fix it.
SELECT
src.StockId, src.Seq, src.SeqCount, src.Make, src.Color, src.ActionType,
CASE WHEN src.LeadValue = 'Sale' AND src.ActionType IS NULL THEN 'Quote' ELSE src.ActionType END dActionType,
src.ActionDate, src.LeadValue, src.LagValue
FROM
(
--Dataset transformation
SELECT
src.StockId,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER (PARTITION BY StockId ORDER BY ActionDate DESC) Seq,
COUNT(*) OVER (PARTITION BY StockId) SeqCount,
src.Make, src.Color, src.ActionType, src.ActionDate,
LEAD(ActionType) OVER (ORDER BY ActionDate DESC) LeadValue,
LAG(ActionType) OVER (ORDER BY ActionDate DESC) LagValue
FROM #SampleDataSet src
) src
WHERE 1=1
Here is the output;
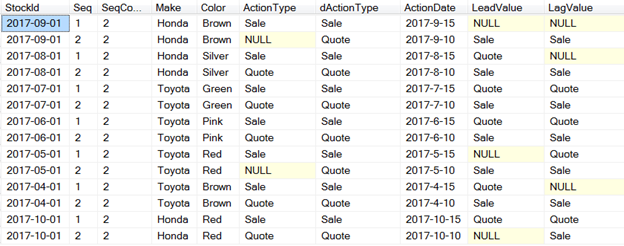
dActionType is a derived column that has all the correct sequence of actions with the help of Lead() and LAG() function.
Resources
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/functions/lead-transact-sql?view=sql-server-2017
This is tricky. Azure PaaS (Platform as Service) SQL Database has master database only. If programmer is taking any advantage of MSDB databases or synonymous, it will not work there directly.
Use Deploy Database to Microsoft Azure SQL Database
The simple method to restore to Azure SQL Database is;
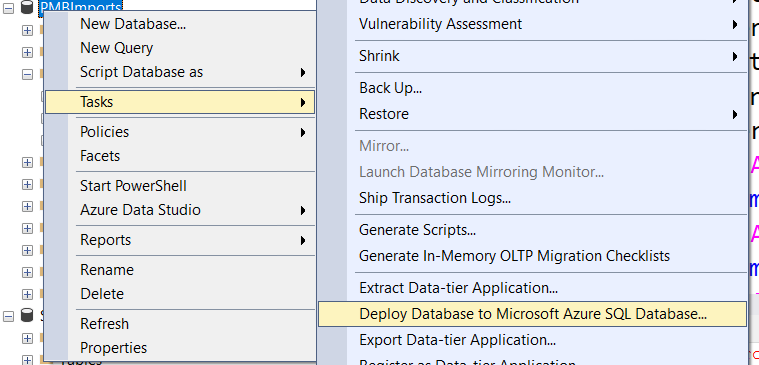
This will create a new database on Azure SQL Server. You can rename it to your actual database.
Migrate to Azure SQL by restoring from Database
This method requires Azure storage account.
Create a blob storage. Upload database backup. From SQL Management Studio, right-click to [YourLOCALDatabase] and open Tasks>Export Data-tier Application. You can export your database to Azure Blob Storage on this wizard. After backup, connect your Azure SQL Server from SQL Management Studio. Go to your [YourREMOTEDatabase], right-click Databases folder from treeview and go to Import Data-tier Application. Choose your backup file from Blob Storage and enjoy!
This will create a new database on Azure SQL Server. You can rename it to your actual database.
Use Azure Data Migration Assistant Tool
This is unlike other methods mentioned above. This is the most efficient tool for migration databases to Azure SQL. This gives you a chance to select individual objects (tables, stored procedures, views, functions etc). Here is the link;
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53595
This does not create a new database but copy schema and data to existing database.
Use 3dr party tool
3rd party tools can be used to backup/restore Azure SQL database. Here is the list;
The tool allows us to create azure backup on local/remote. We can restore those backups on local/remote machine. I have a schedule job on my local that run everyday 10:00AM to create full backup in Azure blob container “myContainer”.
This tool also allows you to backup on your local computer.
Other methods that can be used with Azure SQL Database;
Use if you need to move data from Azure to a specific destination (e.g. your old SQL Server) or in a particular format (e.g. flat file) with SQL Server Management Studio tools
Similar to SQL Server Import and Export Wizard, but enables automatic process
Use when you need to create BACPAC file with SQL Server Management Studio tools
Use if you need to create BACPAC file from a command line
Use if you need to save data from one or several tables in a readable format
Use when you need to perform automatic backups into BACPAC file regularly
Suitable if you only have a browser
Use AzCopy
This tool can be used to transfer data between storage accounts. Here is the link;
https://adamtheautomator.com/azcopy-setup/
Azure Storage Explorer
This is a GUI that can be used to move files between storage accounts and premises. Here is the link;
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/features/storage-explorer/